- Astronomik Lunar calendar for 2024
The Astronomik calendar of the Lunar phases in 2024 is ready.
- Chistmastime and New Year 2023-2024
We wish you a merry Chirstmastime and a happy and healthy 2024...
- Astronomik Lunar calendar for 2023
The Astronomik calendar of the Lunar phases in 2023 is ready.
- Chistmastime and New Year 2022-2023
We wish you a merry Chirstmastime and a happy and healthy 2023...
- Shipping methods
Shipping as registred good shipment is no longer available
- How to observe planetary nebulae
A very nice introduction to observing planetary nebulas written by Owen Brazell
Astronomik OIII Filter

Click the image for full resolution
From the start, the Astronomik OIII filter has been very specifically designed for the visual observation of gaseous and planetary nebulae. The extremely narrow pass band of the two OIII lines brings a substantial contrast gain to these lines even under best observation conditions. On faint super nova remnants and faint planetary nebulae the Astronomik OIII filter will often make the difference as to whether the object can bee seen or not!The optimal aperture ratio for the use of the filter is 1:3.7 to 1:15 with apertures of more than 6" (150mm). Transmission losses and chromatic distortions, which arise with other filters, occur with Astronomik OIII filters only when extremely bright aperture ratios of 1:3 and more come into play. The Astronomik OIII filters thus can expand the view of dispersed objects, generally speaking, to the whole visual field of view of the eyepiece and are not limited to only the center of the eyepiece.
Main use
Since enough light must be available to make use of the OIII filter it is best to use this filter with apertures of more than 6" (150mm). Smaller instruments do not gather enough light for meaningful and satisfying astronomical work. However, please note: Many experienced Deep Sky observers, with apertures of more than 10" (250mm), prefer using the OIII filter instead of the more versatile UHC filter. Due to the high optical quality of the Astronomik OIII filter substrate you will see the same needle-sharp stars as you would from your regular telescope.
more information about the visual Astronomik filters
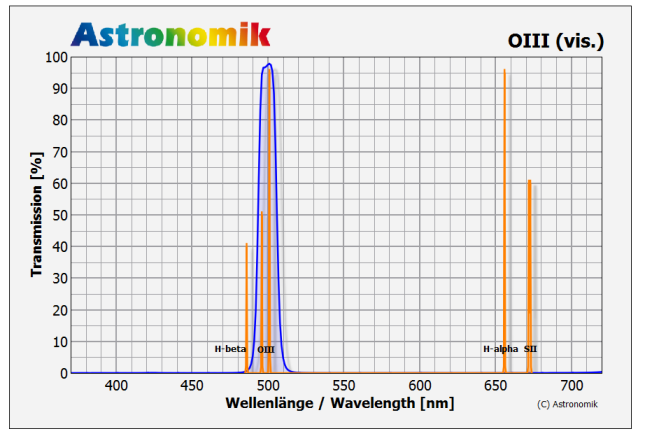
How to read the chart
The major emission lines of artifical light pollution:
| Hg 435,8nm | Hg 546,1nm | Hg 577,0nm | Hg 578,1nm |
| Na 589,0nm | Na 589,6nm | Na 615,4nm | Na 616,1nm |
The major emission lines of nebulas:
H-β 486,1nm | OIII 495,9nm | OIII 500,7nm | H-α 656,3nm
- The horizontal axis is the Wavelength in Nanometers (nm). 400nm is deep blue, at 520nm the human eye senses green and at 600nm red. At 656nm is the famous "H-Alpha" emission line of hydrogen.
- The transmission in % is plotted on the vertical axis.
- The red line shows the transmission of the filter.
- Visual filters: The grey line in the background shows the relative sensitivity of the human eye at night. The maximum is at ~510nm and drops to longer and shorter wavelengths. You can easily see, that you can´t see anything of the H-alpha line at night (even if you can during daylight!) The sensitivity at 656nm is 0% at night!
- Photographic filters: The grey line in the background shows the sensitivity of a typical CCD sensor.
- The most important artifical emission lines are shown in orange. The artifical light pollution is dominated by see mercury (Hg) and sodium (Na), which are used in nearly all streetlights.
- The most important emission lines from nebulas are shown in green. The most important lines are from ionized Hydrogen (H-alpha and H-beta) and double ionized oyxgen (OIII).
The major emission lines of artifical light pollution:
| Hg 435,8nm | Hg 546,1nm | Hg 577,0nm | Hg 578,1nm |
| Na 589,0nm | Na 589,6nm | Na 615,4nm | Na 616,1nm |
The major emission lines of nebulas:
H-β 486,1nm | OIII 495,9nm | OIII 500,7nm | H-α 656,3nm
Suitability
- Visual observation (dark skies): Very good, huge contrast enhancement at O III-emission nebulas
- Visual observation (urban skies): Very good, huge contrast enhancement at O III-emission nebulas
- Film photography: It depends, very long exposure time
- CCD photography: Good, when used with an additional IR-block-filter
- DSLR photography (original): Very good, huge contrast enhancement at O III-emission nebulas
- DSLR photography (astro modified): Very good, huge contrast enhancement at O III-emission nebulas
- DSLR photography (MC modified): Good, when used with an additional IR-block-filter
- Webcam / Video (Planets): Unsuitable
- Webcam / Video (Deep Sky): Reasonable, if light pollution is a big problem and OIII Objects are beeing observed
Technical Data
- typ. 95% transmission at 496nm (OIII)
- typ. 95% transmission at 501nm (OIII)
- Complete blocking of all disturbing wavelength coverages
- The ideal filter for telescopes 10 " (25cm) and larger
- Main operational use: Planetary nebulas & super nova remnants
- No moisture-sensitivity, no aging, and totally scratch-proof
- Excellent carrier material - substrate is optically polished. The optical performance (resolution & contrast) of your telescope is not reduced in any way by the filter.
- Parfocal with other Astronomik filters
- Glass thickness: 1mm
- Completely resistant against high humidity, scratches and aging effects
- Diffraction limited, the filter will not reduce the optical performance of your telescope!
- Astronomik filters are delivered in a high-quality, long lasting, filter box
Customer Testimonial
John C.: "I bought your 2'' visual OIII filter from OPT and found it superior to the others I have tried. No red dots. Excellent contrast in the veil nebula. Thank you for making such a fine filter!"
The filter is available in the following sizes
Filter displayed products below by their features
- Remove This Item Size: T-thread cell (M42x0,75)
- Center-Wavelength
-
- OIII (501nm) (1)

 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English